
At the end of their lifecycle, fixed assets are often converted into cash. Many organizations choose to present capitalized assets in various asset groups. It is common to segregate fixed assets on the balance sheet by asset class, such as buildings or equipment, as separate lines on the balance sheet.
Moreover, the reports are also necessary to determine whether to lend money or purchase shares in that company. The phrase fixed asset means that these holdings are not supposed to be utilised within the financial year. Fixed assets have a materialistic form and are shown on a balance sheet in the form of PP&E. Generally, a fixed asset is purchased for the supply and manufacturing of commodities and services.
Maintaining Accurate Records
If the laptop is being used in a company’s operations to generate income, such as by an employee who uses it to perform their job, it may be considered a fixed asset. In this case, the laptop would be recorded on the company’s balance sheet as property, plant, and equipment (PP&E). However, if the laptop is being used for personal use, it would not be considered a fixed asset and would not be recorded on the company’s balance sheet.
Some companies elect to merge this account into the Furniture and Fixtures account, especially if they have few office equipment items. If an asset meets both of the preceding criteria, then the next step is to determine its proper account fixed asset accounting classification. Here we will look at a real-life example that is easy to grasp using the straight-line method of depreciation. With the inability to track assets comes the consequence of facing huge losses from theft or misplacement.
Key Features of Fixed Asset Management Software
The major difference between fixed and current assets is that fixed assets cannot be easily converted into cash, and current assets can be turned into cash within twelve months. An example of a fixed and current asset is office furniture and inventory, respectively. Assets are those which indicate those items or resources owned by the firm.
This means that its recorded value on the balance sheet is adjusted downward to reflect that it is overvalued compared to the market value. Many organizations would not exist or generate revenue without their property, plant, and equipment. To understand accounting and financial reporting, begin with a broad-level knowledge of fixed assets.
Benefits of Fixed Asset Management
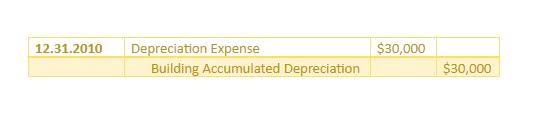
In order to maintain precise financial reports, firms need to oversee all work processes regarding fixed asset usage. Over the years, the accumulated depreciation balance continues to increase in value until it equals the total cost of the fixed asset. At this stage, you can stop accounting for depreciation and formally retire the asset.
- Impairment is present when an asset’s carrying amount is greater than its undiscounted future cash flows.
- Fixed assets generally appear as ‘Property’, ‘Plant’, and ‘Equipment’ (PP&E) on a balance sheet of an enterprise.
- Fixed asset accounting can be complex, and companies may face several challenges when tracking and managing their fixed assets.
- A fixed asset is, more often than not, a finite, long-term investment.
- Investors and creditors use these reports to determine a company’s financial health and decide whether to buy shares in or lend money to the business.
- The computer equipment account can include a broad array of computer equipment, such as routers, servers, and backup power generators.
- In accounting, a fixed asset, also known as a capital asset or tangible asset, is a tangible long-lived piece of property or equipment a company plans to use over time to help generate income.

